We’re here to help answer your questions. Browse the frequently asked questions below, and if you don’t see what you’re looking for, contact us online or call 1-800-632-6605.
General Questions
What is on-site generation?
On-site generation is a service offering that allows Idaho Power customers to install electricity-generation equipment—such as solar panels or other renewable energy systems—at their home or business to offset some of their energy use while staying connected to Idaho Power’s grid.
With an interconnected system, energy flows both ways-between your home and the grid. At times, your system may produce more energy than the home/business needs. At other times, the home/business will need more electricity from Idaho Power. Alternatively, systems can be designed as ‘non-export’, meaning any excess energy is prevented from flowing back to the grid.
Which Idaho and Oregon customers are eligible, and what are the size limits?
Idaho and Oregon residential (Schedule 1) and small general service (Schedule 7) customers may connect energy generation sources (e.g. solar) with a total nameplate capacity of 25 kilowatts (kW) AC or less. They may also connect energy storage (e.g. batteries). *
Idaho and Oregon large general service (Schedule 9), large power (Schedule 19) and irrigation (Schedule 24) customers may connect an exporting system with a total nameplate capacity equal to or less than the greater of: (a) the greatest monthly Billing Demand established during the most recent 12- month period which includes and ends with the current Billing Period, or (b) 100 kW. Customers may also connect energy storage (e.g. batteries).*
*Energy storage devices do not count toward the maximum allowable capacity noted above; however, AC-coupled energy storage devices will count toward the total capacity for the Feasibility Review.
For exporting systems over these limits, refer to Generator Interconnection.
What are Idaho Power’s rules for Idaho customers?
All customer generation systems and energy storage systems must satisfy the requirements of Schedule 68 Interconnections to Customer Distributed Energy Resources. Upon completion of the interconnection process, customers with Exporting Systems will take service under one of the following schedules in Idaho Power’s tariff:
- Idaho residential customers – Schedule 6, Residential Service On-Site Generation
- Idaho small general service customers – Schedule 8, Small General Service On-Site Generation
- Idaho large general, irrigation and large power customers – Schedule 84, Large General, Large Power, and Irrigation On-Site Generation Service, and their standard retail service schedule (i.e. Schedule 9: Large General Service).
For Idaho residential (Schedule 6) and large general service (Schedule 9) customers, upon completion of the interconnection process, customers will take service under the Standard Rate option. Customers may request to transition to the Time of Use option if applicable after receiving final permission to operate by contacting the customer service center.
What are Idaho Power’s rules for Oregon customers?
All customer generation systems and energy storage systems must satisfy the requirements of Idaho Schedule 68, Interconnections to Customer Distributed Energy Resources. Upon completion of the interconnection process, customers with exporting systems will take service under one of the following schedules in Idaho Power’s tariff:
Oregon residential customers
- Monthly charge values are listed in Oregon Residential Service (Schedule 1). Reference the “Monthly Charge” section.
- Service terms and Export Credit Rates are listed in Idaho Schedule 6, Residential Service On-Site Generation. (Charges in Schedule 6 apply to Idaho customers only.)
Oregon small general service customers
- Monthly charge values are listed in Oregon Small General Service (Schedule 7). Reference the “Monthly Charge” section.
- Service terms and Export Credit Rates are listed in Idaho Schedule 8, Small General Service On-Site Generation. (Charges in Schedule 8 apply to Idaho customers only.)
Oregon Large general, irrigation and large power customers
Service terms and Export Credit Rates are listed in Idaho Schedule 84, Large General, Large Power, and Irrigation On-Site Generation Service.
Service terms and monthly charge values are listed in the applicable Oregon Large General, Large Power and Irrigation Service (Schedule 9, 19, and 24)
When do solar panels produce energy?
Solar panels only produce energy in natural daylight. They do not produce energy at night, and production may be limited on cloudy days. Panels also are incapable of storing energy. Solar panels can be paired with energy storage systems such as batteries to store a limited amount of energy for use at a later time.
Will on-site generation lower my electric bill?
The monthly electric bill for homeowners who install solar or wind may be lower because of the energy they receive from their system. But solar and other renewable generation systems can be a large investment, costing thousands — often tens of thousands — of dollars. So, while your electric bill may be lower each month, you won’t see a true return on your investment for years down the road. Additionally, there are different payment options for solar, including paying cash upfront or financing plans that include interest. Typically, any time a large purchase requires making monthly payments, interest charges are included. Adding interest increases the total cost and length of time to recoup an investment. To help you make an informed decision about solar, access our online solar calculator near the bottom of our Investing in Solar webpage.
What factors affect payback for a solar on-site generation system?
Many factors can affect the payback, including the cost per watt of the system, its energy production, the export credit value, and your tax credit eligibility. A system’s energy production depends on the technology used, how the system is configured, and environmental factors. Solar production is affected by the direction and tilt of the panels and anything that causes shade, including clouds and dust. Wind production is affected by location, turbine height, and obstacles that interrupt wind flow, such as nearby structures or trees. Another factor is electricity price changes. Idaho has some of the lowest electricity prices in the nation, largely due to our clean, low-cost hydroelectric system. Prices fluctuate slightly year-to-year due to inflation, fuel costs and other factors. Utility bill increases 1.81% per year based on historical data in Idaho Power’s Integrated Resource Plan (IRP). Additionally, Idaho Power’s rules and pricing structures are not contracts and are subject to change at any time with approval from the IPUC. Modifications to the compensation structure could result in changes to how excess energy sent back to the grid by the customer is measured and credited and the value of that credit. Those changes could impact any savings realized from a rooftop solar system and potential payback on the investment.
Will solar or other renewable generation keep my power on during an outage?
Generally, no. Having power when the grid is down requires a battery backup system. Inverters are the part of a typical solar system that converts DC power to usable AC power. The vast majority of inverters are grid-connected and work only if the electrical grid is functioning normally. If the grid experiences an outage, the inverters sense the abnormality and will stop interacting with the grid. This helps keep work crews safe and the grid stable. A small number of customers connect to the grid and have a battery backup system. This allows them to use energy stored in the batteries while the power is out. Battery backup systems will add cost to the overall system.
If I install solar or wind, do I still need power from the utility?
Most homeowners with on-site generation connect to Idaho Power’s electrical grid to ensure reliable, consistent electricity. The wind doesn’t always blow. Solar panels only produce when the sun is out. Even then, the panels may not produce enough energy to meet the home’s energy needs. The grid lets solar customers draw power at night when there is no sunshine, during a cloudy day, or any time they need more electricity than their system is generating. Also, most customers with on-site generation rely on the grid for the rush of power needed to start up large appliances like air conditioning units. Without the grid, the average solar or wind generation system can’t supply enough instantaneous power to turn on these large appliances. For these reasons, homeowners with on-site generation rely on Idaho Power’s electrical grid every hour of every day.
What type of renewable on-site generation systems are allowed?
Currently, solar photovoltaic (PV) is the most common choice for those who generate their own renewable energy. However, Idaho Power’s on-site generation tariffs allow customers to connect solar, wind, small-scale hydro, biomass, geothermal and fuel cell technologies as exporting systems. Other fuel types and stand-alone energy storage are allowed as non-exporting systems.
How much space do I need?
For a solar array, each kilowatt (kW) DC of solar photovoltaic generation capacity requires about 100 to 200 square feet of roof or ground area depending on the efficiency of the panels. For a wind turbine, the space depends on the type and height of the system installed. A general rule of thumb is the turbine generator should be 20 feet above the top of anything within 300 feet of the system. Turbines should be erected away from structures to minimize the risk of falling on buildings during strong winds. The minimum distance between turbines and structures is typically equal to the combined height of the tower and blades, known as the “fall distance.”
What size system should I get?
The size of the system depends on many factors including your goals, the type of generation technology and its output, the available space and how much energy your home or business uses. Before you decide on a size, consider taking advantage of Idaho Power’s energy efficiency programs to help lower your overall energy use. Reducing your energy needs may allow you to install a smaller system and save money and is also your greenest option.
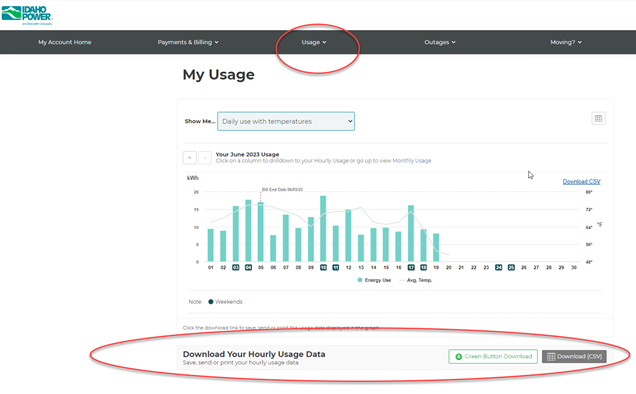
How do I access my energy usage data?
Customers can access their monthly and hourly energy usage through My Account, Idaho Power’s online customer information portal. To access usage data, log in to My Account and select Usage on the top menu bar. Choose My Energy Usage from the drop down and look for the buttons to Download Your Hourly Usage Data below the graph. Monthly energy use is also displayed on your monthly billing statement.
How is system size determined?
For inverter-based generation sources, the total nameplate capacity is defined as the AC nameplate rating of the inverter. For non-inverter-based generation sources, the nameplate capacity is defined as the nameplate rating of the generation source (example: nameplate rating of a wind turbine).
When an energy storage device is paired with a generating system, the total nameplate capacity depends on whether it is DC-coupled or AC-Coupled. For example, if a battery storage device uses the same inverter as the solar generation system, it is DC-Coupled. If the solar system and battery have separate inverters, the battery is AC-coupled. The total system size for generation systems with energy storage devices will be calculated as follows:
- DC Coupled: For energy storage devices that are DC coupled, the total nameplate capacity of the system is defined by the inverter (kilovoltampere [kVA]).
- AC Coupled: For AC coupled energy storage with an exporting system, the total nameplate capacity is the total nameplate capacity of the generation system plus the energy storage system on the customers’ side of the interconnection point (i.e., the AC capacity of the solar PV system plus the AC capacity of the battery.)
For exporting systems, energy storage capacity shall not be used to calculate the allowable capacity limits set in Schedules 6, 8 and 84. AC coupled storage will count towards the total nameplate capacity values used for Feasibility Reviews for exporting systems as outlined in Schedule 68.
Energy Storage installed without a generating source must be installed as a non-exporting system under the rules of Schedule 68. (See Non-Export section below for more details).
How does net billing work?
Net billing charges customers for all kWh consumed from the grid at the retail rate and compensates customers for all kWh exported to the grid at the ECR. Importantly, the customer first uses all energy generated from their system to offset their own energy needs, which reduces the amount of energy they consume from the grid. Under net billing, the netting occurs on the bill – after 100% of consumption and 100% of exports are assigned a monetary value. ECR values are listed in Idaho Rate Schedules 6, 8, and 84. Idaho customers’ pricing is listed in the applicable Idaho Rate Schedule 6, 8, 9, 19, and 24. Oregon customers’ pricing is listed in the applicable Oregon Rate Schedule 1, 7, 9, 19, or 24.
What is the current export credit rate (ECR)?
The following are the ECR and seasonal variation details copied from the on-site generation schedules 6, 8, and 84. Additional details including defined terms and credit treatment are provided in these schedules. Links to the schedules can be found on our Understanding Customer Generation web page.
Summer and Non-Summer Seasons
The summer season begins on June 1 and ends on Sept. 30 each year. The non-summer season begins on Oct. 1 and ends on May 31 each year.
| Summer On-Peak | Summer Off-Peak | Non-Summer |
|---|---|---|
| 15.6836¢ per kWh | 3.3920¢ per kWh | 2.9019¢ per kWh |
Time Periods
The time periods for the ECR are as follows. All times are stated in Mountain Standard Time.
Summer Season ECR
On-Peak: 3 p.m. to 11 p.m. Monday through Saturday, except holidays
Off-Peak: 11 p.m. to 3 p.m. Monday through Saturday, and all hours on Sunday and holidays
Non-Summer Season ECR
Off-Peak: All hours Monday through Sunday
Holidays are New Year’s Day (January 1), Memorial Day (last Monday in May), Independence Day (July 4), Labor Day (first Monday in September), Thanksgiving Day (fourth Thursday in November), and Christmas Day (December 25). If New Year’s Day, Independence Day, or Christmas Day falls on Sunday, the following Monday will be designated a holiday.
ECR, per kWh
The following rate structure and credits are subject to change upon commission approval:
How is the ECR determined?
The ECR approved by the IPUC, which follows an established methodology, is reflective of the value of customer generation exports to the grid based on the time and day the energy is generated.
In developing the ECR, Idaho Power implemented a repeatable method that relies on recent data to ensure timely recognition of changing conditions on Idaho Power’s electrical grid and broader power markets. Generally, Idaho Power relied on avoided cost principles as a foundation for the ECR including avoided energy costs, avoided generation costs, avoided or deferred transmission and distribution costs, avoided line losses, and integration costs. The ECR is subject to change following the IPUC’s review and approval. The current ECR will be maintained until Idaho Power proposes updates to it as part of an April 1, 2028 filing, at which time subsequent updates to the ECR may occur annually.
How much energy does a system generate?
The energy generated varies by the type of system and depends on such factors as technology, age, weather, location and directional orientation. Solar panels do not produce the same amount of power at all times of the year or all times of the day. They produce less in the winter due to the weather and fewer hours of daylight. Energy generated will vary depending on the time of day, cloud cover and shading from nearby trees, roof pitches or other structures. The times that solar energy is generating doesn’t always align with when the home needs energy. PVWatts Calculator is an online tool developed by the federal government for estimating solar generation based on geographic location and system design. To use PVWatts to evaluate different system sizes, input your city, solar size in kilowatts (kW) and the calculator will estimate solar electricity generation by hour for a full year.
How can I get the most from my system?
Your system first powers your home or business directly, which reduces the amount of energy you purchase from Idaho Power. Any extra energy you produce goes to the grid, and you’re credited based on the Export Credit Rate (ECR).
Understanding how and when your home or business uses energy and comparing that to the ECR, is key to maximizing your system’s value. Idaho Power’s online MyAccount tool allows customers to access a variety of information about their account. With Idaho Power’s My Account tool you can:
-Download your hourly meter data, view past bills, and more!
-Track when you’re using energy from the grid vs. when you’re sending energy back
-View your usage by hour, day, month, or year.
How is on-site solar different from utility-scale solar?
On-site solar projects are smaller systems (typically less than 25 kW for residential), located behind a customer’s meter, and designed to offset all or a part of a customer’s energy needs. Utility-scale solar generally refers to systems larger than 10 megawatts, is tied directly to the grid, and serves all customers. Utility-scale solar—or any utility-scale resource—typically has a lower installation cost per kW of capacity.
How does on-site solar contribute (or not) to Idaho Power’s clean energy goal?
While Idaho Power customers with on-site generation are generating and using clean energy, it isn’t included in Idaho Power’s energy mix (and, therefore, doesn’t technically count toward our company’s clean energy goal). That’s because the customer uses most of the energy produced by on-site generation. Any excess net energy helps from an avoided cost perspective (i.e., energy Idaho Power doesn’t have to produce elsewhere), but because it is for the customer’s use and they are compensated for any excess energy, it does not count toward our company’s energy mix.
Does Idaho Power offer any financial incentives or rebates for installing small-scale renewable energy systems on my property?
No. However, there are federal and state tax incentives and loan programs that may help with financing on-site renewable energy sources. The Idaho Office of Energy and Mineral Resources has information on financing options at oemr.idaho.gov. For Oregon customers, visit the Oregon Energy Department at oregon.gov/energy. The Database of State Incentives for Renewable Energy (DSIRE), funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, also lists incentives for renewable resources by state at dsireusa.org.
Connecting Your System
How do I get started?
Use our Solar Checklist to help you plan and decide if solar is right for you. If you decide to install solar, visit our Apply to Connect Your System webpage to see an overview of Idaho Power’s interconnection process and complete the required application.
Is there any special equipment required?
Solar, wind and other forms of energy generation are electrical sources and must be designed with safety in mind. In general, we require a grid-tied smart inverter. Smart inverters must conform to the latest Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 1547 standards and be certified by the Underwriters Laboratory (UL) 1741 standard, which complies with the latest IEEE 1547 standards. Idaho Power requires smart inverters that comply with IEEE 1547-2018 and are UL 1741 SB certified. Idaho Power also requires an AC disconnect switch on the customer’s side of the meter. Breakers do not meet these requirements. AC disconnects and meters must be readily accessible to Idaho Power 24/7. An overview of the interconnection requirements and a link to the rules as outlined in Schedule 68 Interconnections to Non-Utility Generation are available at idahopower.com/customerGeneration. The specific requirements for the AC disconnect are listed in Schedule 68. Making changes to an existing service will require the service to comply with the current Customer Requirements for Electric Service, including requirements for service and panel upgrades and meter accessibility.
What is a smart inverter?
- Smart inverters must conform to the latest Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 1547 standards and be certified by the Underwriters Laboratory (UL) 1741 standard, which complies with the latest IEEE 1547 standards. Idaho Power requires inverters that comply with IEEE 1547-2018 and are UL 1741 SB certified.
- System Modifications that (1) do not replace or add inverters, (2) are like for like as the result of warranty inverter replacements, or (3) rely on an inverter that is required to meet the original inverter specifications for the Customer Generator System to properly function, may be considered exempt from the smart inverter requirement.
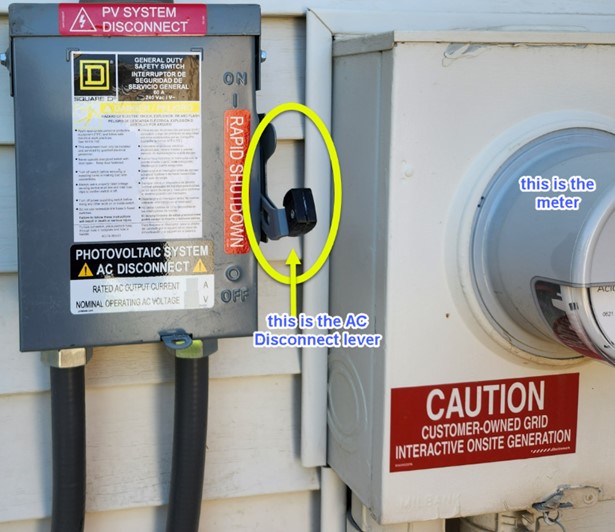
What is an AC disconnect switch?
- Idaho Power requires a safety disconnect switch to disconnect generation or energy storage systems from our distribution system to ensure the safety of our line workers. This switch stops the alternating current (AC) power from your solar or battery system from traveling through the Idaho Power meter to the electrical grid. It is typically located next to your Idaho Power meter and has a lever that can be moved to the “off” or “on” position. The “off” position disconnects your on-site system from Idaho Power’s meter and electrical grid. Below is a picture of a typical AC disconnect.
- For the full AC disconnect requirements, reference the “Disconnect Equipment” section of Schedule 68 – Interconnections to Customer Distributed Energy Resources.

What fees does Idaho Power charge to connect a system to the grid?
Idaho Power requires a non-refundable $100 fee to cover application processing, engineering review and on-site inspections. If the project requires upgrades to Idaho Power equipment, the applicant also must pay those costs. The first Idaho Power inspection is conducted at no charge. A return trip charge of $52 may be billed to the customer each time Idaho Power personnel are dispatched to the job site but are unable to conduct the on-site inspection due to one or more of the conditions not being met that had been certified as complete by the customer or customer’s representative on the System Verification Form. This charge will appear on the customer’s bill the following month. Making changes to an existing service requires the service to comply with the current Customer Requirements for Electric Service. There may be additional costs, if you upgrade your service or panel or if your meter does not meet the accessibility requirements.
What are common reasons a return-trip fee is charged for a certification inspection?
For new on-site generation systems going through Idaho Power’s interconnection process, the first inspection is conducted at no charge. A return trip charge of $52 may be billed to the customer each time Idaho Power personnel are dispatched to the job site but are unable to conduct the on-site inspection due to a condition not being met that had been certified as complete on the System Verification Form. Here are common reasons Idaho Power’s on-site inspection cannot be completed and a return trip fee may be charged:
- The generation system installation was not finished.
- The system does not generate. This is usually due to a breaker being off or an issue with the inverters (e.g., inverters were not programmed, were not turned on, or have a fault).
- During the grid outage simulation, the inverter reconnects faster than the required 5-minute delay.
- There is no AC disconnect for the generation system or the AC disconnect does not meet the requirements in Schedule 68.
- The AC disconnect and meter are not accessible (behind a locked gate or in a building).
- A battery storage system was installed but not disclosed on the System Verification Form.
- The battery storage system is not working.
What happens if I don’t comply with Idaho Power’s interconnection tariffs?
On-site generation that is interconnected to Idaho Power’s electrical grid must comply with the rules for interconnection. These requirements ensure the safety of Idaho Power crews working in the area and protect the reliability of the electrical grid for all customers. Customers with generation systems found to be interconnected without completing the Customer Generation application process will be asked to bring their system into compliance or risk being permanently disconnected from the electrical grid.
What if my system uses batteries and/or energy storage devices?
There are two configurations for energy storage devices (such as batteries): those that share an inverter with a generation facility (direct current [DC] coupled); and those that have a standalone inverter (alternating current [AC] coupled). For exporting systems, both configurations may export power onto Idaho Power’s system once the customer has completed the interconnection process. Energy storage devices not coupled with a generation facility taking service under Schedule 6, 8, or 84 (exporting system) may not export energy onto Idaho Power’s system and must take service under the non-export provisions of Schedule 68.
What happens if I change the installation company representing my project?
If you choose to change your contractor or project representative, a new application and processing fee will be required. Expect contact from Idaho Power asking to confirm which application will move forward. Once confirmed, Idaho Power will withdraw the application that is not being used and redo the feasibility review.
What is an Incomplete Application?
An application is incomplete if it’s missing any information needed to satisfy the requirements of the customer interconnection process. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Customer/applicant signature and/or initials
- Non-refundable application fee
- Details about the proposed system
If an application is incomplete, you have 60 days from the date your application was received to provide the missing information. If the application remains incomplete after 60 days, it will be considered withdrawn, and you will need to submit a new application and application fee to proceed.
Managing Your System
How is real-time billing presented on my monthly bill?
Watch this video for a tutorial on reading your on-site generation bill.
Please note example bills in the video are for informational purposes only and do not reflect current pricing.
What if I want to expand or modify my system?
Modifications to customer generation systems that increase the total nameplate capacity of the system or modify the system in any way (including inverter replacements) that may impact the safety or reliability of Idaho Power’s electrical system are considered system modifications. Customers planning modifications must complete the interconnection process including a new application, $100 fee and system verification form. Common modifications requiring an application include:
- Inverter additions or changes (including like for like and warranty replacements or installing a different inverter model)
- Module replacements or additions that increase the total DC capacity for systems originally approved before May 1, 2020.
- Adding energy storage (batteries)
Some scenarios do not require an application and fee, but Idaho Power does require that customers fill out a new system verification form notifying us of the change. Scenarios include:
- Module changes for systems approved after May 1, 2020
- Battery replacements (like for like) or removal
- Removing inverters (and not replacing)
If you aren’t sure, please reach out to cg@idahopower.com to determine if an application is needed.
Note: Systems applying for modifications must meet the requirements in place today. Modifications may also require a state/city electrical inspection. Be sure to check with your authority-having-jurisdiction to ensure the work complies with all electrical codes.
System Modifications that (1) do not replace or add inverters, (2) are like-for-like as the result of warranty inverter replacements, or (3) rely on an inverter that is required to meet the original inverter specifications for the customer generator system to properly function, may be considered exempt from the smart inverter requirement.
How do I know if my system has Legacy status?
Idaho Residential and Small General Service (Schedules 6 and 8):
- Customers who interconnected their system by December 20, 2019, or
- Customers who submitted an on-site generation application on or before December 20, 2019, and provided evidence of a binding financial commitment for the on-site generation system by January 19, 2020, and who completed the interconnection process by December 20, 2020.
- Residential and Small General Service Legacy status will terminate December 20, 2045.
Idaho Large Commercial, Industrial and Irrigation (Schedule 84):
- Customers who interconnected their system by December 1, 2020, or
- Customers who submitted an on-site generation application on or before December 1, 2020, and interconnected their system as a two-metered system by December 1, 2021.
Large Commercial, Industrial, and Irrigation Legacy status will terminate December 1, 2045.
Oregon Customers (Schedule 84):
- Oregon customers who interconnected their system by June 1, 2024, or
- Oregon customers who submitted an application to Idaho Power by June 1, 2024, and complete the interconnection process by their application’s expiration date.
- Legacy status will terminate December 1, 2045.
A customer may elect to forfeit a system’s Legacy status. After forfeiting Legacy status, the system would receive the Net Billing compensation structure under the applicable on-site generation offering, Schedule 6, 8 or 84, and would be subject to future changes in the compensation structure. Please note–customers with an Idaho Power generation meter dedicated to the Legacy system would be required to rewire the system behind the Idaho Power service meter. To forfeit Legacy status, submit a written request to Idaho Power:
Email: cg@idahopower.com
Mail: Idaho Power
Customer Generation, CHQ8
PO Box 70
Boise, ID 83707
Not sure if your system is a Legacy system? Call Idaho Power’s customer solutions advisors at 1-800-632-6605 to confirm your system’s status.
What are the criteria for Legacy systems?
It is the on-site generation system, not the customer, that receives legacy status at the meter site and at its originally installed nameplate capacity. A customer who moves into a property with a legacy net-metering system will inherit the legacy system. When a customer moves from a property with a legacy system, that customer does not get to take the legacy status of the system with them to their next property. If a system is offline for more than six months, or is moved to another site, the legacy status of the system is forfeited. If a customer expands their system, the expansion must be metered separately to retain the legacy status of the original system. If the expansion is not metered separately, the entire system will lose legacy status. To allow for the replacement of degraded or broken panels, the customer may increase the capacity of their legacy system by no more than 10% of the originally installed nameplate capacity or 1 kilowatt, whichever is greater.
Are there special installation requirements for expansions to Legacy systems?
Modifications to Legacy systems are allowed; however, if generating capacity is added, the way in which the new system is connected to the grid could result in forfeiture of the Legacy status of the existing system. The added generation system (i.e. both the new panels and associated inverters) must be metered separately from the Legacy system to retain Legacy status for the existing system. The new portion of the system will not receive Legacy status and will take service under the rules in place at that time and will be subject to future changes in the billing and compensation structure. If the generating capacity increases and the expansion is not separately metered from the Legacy system, Legacy status will be forfeited.
What if I want to replace a broken panel?
Non-Legacy systems can replace broken panels following the process for modifying systems. For more information, read the FAQ “What if I want to expand or modify my system?” For Legacy systems, the Idaho Public Utilities Commission allows for replacing degraded or broken solar panels without affecting a system’s Legacy status if specific conditions are met. When replacing panels, customers may increase the Legacy system’s capacity by no more than 10% of the initially installed nameplate capacity or 1 kW, whichever is greater. The total number of panels must remain the same or less than the initially installed system. Customers planning to make system modifications must follow the process for modifying systems. For more information, read the FAQ “What if I want to expand or modify my system?”
What if my system is offline or moved?
Systems that are offline for more than six months will be removed from the on-site generation rate and returned to a standard service rate. The AC disconnect will be locked off and the on-site generation meter exchanged for a standard service meter. If the system is brought back online at a later date or moved to a new location, it must meet the current requirements and complete the interconnection process, including a new application. If a Legacy system is offline for longer than six months, or is moved to another site, the Legacy status is forfeited.
How do I know if my system is working? What if it breaks?
Ensuring your system is operating is your responsibility. Be sure to keep copies of all warranties. Track your monthly energy use and generation (if you have data monitoring) to look for abnormal changes in use. These may indicate an issue. Idaho Power’s My Account online portal has hourly data and will record the excess energy each hour you push power to the grid. If you suspect your system is not working, check to see if the system’s AC disconnect is in the on position and that the breaker is on. You may also need to contact a local licensed electrician or solar installer to have them ensure the inverter is programming is up to date and the inverter is working. For systems that are offline for more than six months, accounts will be moved back to their standard rate schedule and, if applicable, Legacy status will be forfeited.
What if I want to change an existing Large General Service, Large Power or Irrigation Legacy two-meter system into a single-meter system?
Existing customers may choose to convert their existing two-meter design to a single-meter option; however, Legacy status would be forfeited. The customer will be responsible for costs to reconfigure the system and must complete the interconnection process, including a new application.
How can I monitor my energy use and excess energy?
Idaho Power’s My Account tool allows customers to access a wide variety of information including usage data, excess energy delivered to the grid, and even access to past bills. Usage data is provided on an hourly, daily, monthly and yearly basis. Hourly usage data is available for download.
Why doesn’t my excess generation on my bill or in My Account match the production data from my system?
Some systems come with monitors that measure the energy produced by your renewable energy system. These monitors measure the total amount of energy being produced by the system before the energy flows into your home or business. If your system is producing more energy than the home needs at a given moment, the extra energy flows to Idaho Power. Our meters measure that excess energy only.
How should I configure my battery?
For customers with batteries, system configuration and programming will impact how energy is consumed by the home and delivered to grid. Seasonal and time-of-use changes in the ECR will impact the value of exported solar. Work with your battery installer to determine the best configuration for your goals.
Excess Generation Credit Transfers
Can I transfer credits between accounts?
As a customer with on-site renewable generation, you may be eligible to transfer excess generation credits from the on-site generation service (designated) meter to another meter. Both net energy metering (legacy) customers and net billing customers will be eligible for transfer. Meters are eligible to receive credit transfers if they meet the criteria listed in Idaho Power’s Schedule 6, 8, or 84.
Net Billing (non-legacy) customer transfer requirements:
- Excess generation credits (financial) must be available.
- Meters must be held by the customer and be for the customer’s use.
- Transfers can only occur from a designated meter, defined as the meter connected to an exporting on-site generation system.
Net Energy Metering (legacy) customer transfer requirements:
- Excess generation credits (kilowatt-hour [kWh] credits) must be available.
- Meters must be held by the customer and be for the customer’s use.
- Meters must be on the same contiguous property and be served by the same primary feeder as the customer generation (i.e., on-site generation) meter.
- Transfers can only occur from a designated meter, defined as the meter connected to an exporting on-site generation system.
- For transfers from Residential and Small General Service accounts, the receiving meter must be on Schedule 1, 6, 7, or 8. For transfers from Large General, Large Power, and Irrigation accounts, receiving meters must be on Schedules 9, 19, or 24.
- If multiple meters are eligible for aggregation, excess generation credits must first be applied to the designated meter, then to eligible meters outlined above.
It is not necessary to apply for transfer if you wish to retain all credits at the existing meter. Credits that are not transferred will remain with the current service agreement.
What is the process for requesting a transfer?
Fill out the online Excess Credit Transfer Request form during the eligibility window, which opens December 1 and closes January 31 the following year.
Why did I receive a postcard about transferring excess credits? I don’t have credits or additional meters.
In late fall each year, Idaho Power notifies on-site generation customers with excess credits of this opportunity. If you do not meet the eligibility requirements, or do not wish to transfer any credits, no action is needed.
Why am I asked to specify a percent of credit to transfer rather than an actual amount?
Excess Credit Transfer Request forms must be received by Idaho Power by Jan. 31, 2026. After reviewing the eligibility of each request, Idaho Power will execute approved transfers no later than March 31, 2026. Between the time forms are submitted (December through January) and the transfers are executed (March), energy generation and consumption will continue to occur, impacting the available balance of credits. Because it is difficult to predict exact generation and energy use, Idaho Power cannot predict the exact credit balance that will be available at the time of transfer. Therefore, we ask for the percent of the available balance you would like transferred rather than a specific amount.
Where can I find the meter number, service agreement, and other information requested on the form?
Follow this link: How to Read Your Bill – Idaho Power to see an illustration of a bill and where this information can be found. Additionally, you can contact a Customer Solutions Advisor for assistance at 1-800-632-6605.
What if I want to keep some credits at my generation meter?
When you complete the Excess Generation Credit Transfer Request form, you can indicate the percentage of your credit you would like transferred to each eligible meter. If you would only like to transfer a portion of your credit, the percentage requested for transfer can total less than 100%.
It is not necessary to apply for transfer if you wish to retain all credits at the designated meter. Credits do not expire. Credits that are not transferred will remain with the current service agreement.
How will I know if my transfer request has been approved?
If approved, we will email you to let you know during the first week of February. Also, you will see the transfer and transfer fees appear on your March bill statement. The transfer fee is $10 per transfer and will be applied to your customer generation service agreement. If Idaho Power determines one or more of the criteria identified in Schedule 6, 8, or 84 has not been met, you will receive notification by mail, email or phone that the request for transfer was denied.
How will I know how many credits are transferred?
The actual credit transfer will be stated on your March bill for both the customer generation service agreement and the service agreement receiving the transfer.
What if I move before the transfer period?
Net energy Metering (Legacy) customers: Credits are non-transferrable if a customer relocates and/or discontinues service at the point of delivery associated with the exporting system. Any unused credits will expire at the time the final bill is prepared.
Net Billing (Non-Legacy) customers: Credits are transferrable if a customer relocates. If the establishment of service at the new point of delivery is not initiated at the time service at the designated meter is discontinued, it is the customer’s responsibility to request the credit transfer when service is established at the new location in Idaho Power’s service area.
If a customer discontinues services at the Point of Delivery associated with the exporting system and does not intend to establish service at another location in Idaho Power’s service area, any unused credits will be paid out following the time the final bill is prepared.
If I don’t want to transfer credits in March, can I transfer credits later?
No. The rules only allow transfers one time per year and specify the Jan. 31 request deadline and transfer by March 31.
Schedule 68 (Non-export Option)
What is a non-export option? Why is it being offered?
Some customers do not want their generation systems, like solar panels, to export power to the electrical grid and wish to interconnect their system so they consume all energy generated on-site. However, these systems are still grid-connected and, as such, need rules in place to ensure they do not negatively impact the grid. Schedule 68 outlines (1) technical solutions to prevent export; (2) an interconnection and application process so Idaho Power can verify compliance with the interconnection requirements and (3) mitigation efforts should the customer’s system export power beyond the allowable amount, referred to as the inadvertent export limits.
If I choose the non-export option, why are there limits to the generation system size for residential and small general service customers?
Under both the export and non-export options, residential (Schedule 01) and small general service (Schedule 07) generation systems are limited to a maximum AC size of 25 kilowatts (kW) (or kilovoltampere [kVA]). This limit will allow these customer groups to transition between non-export and export (by submitting an application) without making costly retrofits to their systems.
There is no limit to system size for non-exporting systems for large general service (Schedule 09), irrigation (Schedule 24) and industrial (Schedule 19) customers.
Are non-export generation systems subject to different reviews and approvals?
All customer generation applications will undergo a Feasibility Review to determine Idaho Power’s electrical grid’s capability to incorporate the proposed generation system and to determine if upgrades are necessary. In some cases, proposed systems may require an additional Feasibility Study to determine if upgrades or protection equipment is needed. Idaho Power will conduct Feasibility Studies for systems under 3 megawatts (MW) on a case-by-case basis. Systems over 3 MW will require additional study.
What are the approved ways to prevent a generation system from exporting power to the grid?
Advanced Functionality: Use of an internal transfer relay, energy management system or other customer-owned facility hardware or software system(s) to ensure power is never exported across the interconnection point.
Reverse Power Protection: Uses a reverse power relay to ensure power is never exported across the interconnection point.
Minimum Power Protection: Uses an under-power protective function to ensure a minimum amount of power is consumed at all times, and therefore, power cannot be exported.
What if I accidentally export?
Customers whose systems export above the allowed inadvertent export limits (three hours of the distributed energy resource’s total nameplate capacity in any 30-day period) will be notified and expected to take corrective action. For residential (Schedule 01) and small general service (Schedule 07) customers, the inadvertent export must be rectified within 30 days. After 30 days, the customer may elect to turn off the system or move to Schedule 6 or 8 (exporting service). For Schedules other than 1 or 7, the customer must immediately open the AC disconnect until the issue that caused the export is remedied.
For assistance with a PDF on this page or to request a PDF in an alternate format, please contact Customer Service at 208-388-2323 or 1-800-488-6151
